quantitative sample size determination|qualtrics sample size chart : purchasing In brief, a sample size is determined by three elements: i) type I error (alpha); ii) power of the study (1-type II error) and iii) effect size. A proper understanding of the concept of type I error . webShoptime Live no Shoptime: Confira todas as promoções e ofertas que preparamos para vocês! . TV. Eletroportáteis. Cama, mesa e banho. . black friday shoptime; compre na americanas; institucional. trabalhe conosco; relação com investidores; assessoria de imprensa; venda no shoptime; programa de afiliados; cadastro de proteção à .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Na tarde deste sábado (11), o Leão enfrenta o Santa Cruz, às 16h30, na Ilha do Retiro, pela 11ª rodada da competição. E o confronto será transmitido pela TV Globo e DAZN. .
This study aims to explain the importance of sample size calculation and to provide considerations for determining sample size in a simplified manner. Approaches to sample size calculation according to study design are presented with examples in health . In this review, we will discuss how important sample size calculation is for research studies and the effects of underestimation or overestimation of sample size on .
In brief, a sample size is determined by three elements: i) type I error (alpha); ii) power of the study (1-type II error) and iii) effect size. A proper understanding of the concept of type I error . In a recent overview, Lakens (2021) listed six types of general approaches to justify sample size in quantitative empirical studies: (a) measure entire population, (b) resource .Statisticians have devised quantitative ways to find a good sample size. You want a large enough sample to have a reasonable chance of detecting a meaningful effect when it exists but not too large to be overly expensive.
The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math skills. Cochran’s formula is perhaps the most well known equation for calculating .Determination of sample size should begin with a review of the factors covered in Chapter 1. One should have a clear understanding of the following: Objectives of the study: Exploratory . In this article, we'll answer these questions about sample size in quantitative research: Why does sample size matter? How do I determine sample size? Which sampling .
If you want an easier option, Qualtrics offers an online sample size calculator that can help you determine your ideal survey sample size in seconds. Just put in the confidence level, population size, margin of error, and . Determining the sample size in a quantitative research study is challenging. There are certain factors to consider, and there is no easy answer. Each experiment is different, with varying degrees of certainty and .Different survey types may require different approaches to sample size determination. Customer feedback surveys are helpful with smaller sample sizes. Political polls, on the other hand, require larger and more representative samples. Tailor your approach to ensure that the results are statistically sound and reliable.
In this overview article six approaches are discussed to justify the sample size in a quantitative empirical study: 1) collecting data from (almost) the entire population, 2) choosing a sample size based on resource constraints, 3) performing an a-priori power analysis, 4) planning for a desired accuracy, 5) using heuristics, or 6) explicitly .
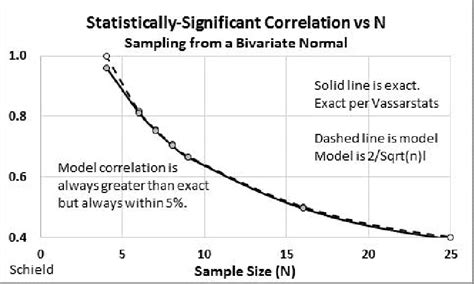
statistically significant sample size
However, if all of this sounds new to you, let's start with what sample size is. Free eBook: The complete guide to determining sample size. What is sample size? Sample size is a term used in market research to define the number of subjects included in a survey, study, or experiment. In surveys with large populations, sample size is incredibly . Determining an appropriate sample size is vital in drawing realistic conclusions from research findings. Although there are several widely adopted rules of thumb to calculate sample size . Both highlight the lack of a priori sample size determination among published articles, but Anthoine et al. (2014) suggest it is due to the lack of accepted and validated ways to calculate the sample size whereas Silva Ayçaguer and Alonso Galbán (2013) argue that such a determination of sample size is unnecessary and even irrational.Determining sample size adequacy for animal model studies in nutrition research: limits and ethical challenges of ordinary power calculation procedures. Int J Food . Power of linkage versus association analysis of quantitative traits, by use of variance-components models, for sibship data. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;66:1616–30. 10.1086/302891 .
What is Sample Size? Sample size is the number of observations or data points collected in a study. It is a crucial element in any statistical analysis because it is the foundation for drawing inferences and conclusions about a larger population.. When delving into the world of statistics, the phrase “sample size” often pops up, carrying with it the weight of your study’s credibility . The determination of sample size in qualitative research introduces a unique and multifaceted challenge, setting it apart from the more structured methodology of quantitative research. Contrary to .
Statistics 514: Determining Sample Size Fall 2021 Example 3.1 – Etch Rate (Page 64) • Consider new experiment to investigate 5 RF power settings equally spaced between 180 and 200 W • Wants to determine sample size to detect a mean difference of D=30 (A/min) with˚ 80% power • Will use Example 3.1 estimates to determine new sample size σˆ2 = 333.7, D = 30, .
Although sample size calculations play an essential role in health research, published research often fails to report sample size selection. This study aims to explain the importance of sample size calculation and to provide considerations for determining sample size in a simplified manner. Approach .4) Use best practice guidelines to calculate sample size. There are many established guidelines and formulas that can help you in determining the right sample size. The easiest way to define your sample size is using a sample size calculator, or you can use a manual sample size calculation if you want to test your math skills. Cochran’s . Background Estimating sample size is an integral requirement in the planning stages of quantitative studies. However, although abundant literature is available that describes techniques for . To calculate your necessary sample size, you'll need to determine several set values and plug them into an appropriate formula. Steps. Part 1. Part 1 of 4: Determining Key Values. Download Article . Example: Sample Size = [z 2 .
Quantitative Sample Size Calculation Methods. Determining an appropriate sample size is crucial for quantitative research, as it directly influences the reliability and validity of results. Sample size estimation begins with understanding the .Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30, 607-610.One of frequently asked question by medical and dental students / researchers is how to determine the sample size. Sample size calculations is necessary for approval of research projects, clearance from ethical committees, approval of grant from funding bodies, publication requirement for journals a .Data entered into a worksheet for Excel sampling: the rows and columns are even. Step 4: Click in the Input Range box and then select your entire data set. Step 5: Click either “Periodic Sampling” or “Random Sampling.” If you choose periodic, enter the nth number (i.e. every 5) and if you choose random sampling, enter the sample size.
Calculate power & sample size for one-sample, two-sample and k-sample experiments. Advanced power and sample size calculator online: calculate sample size for a single group, or for differences between two groups (more than two groups supported for binomial data). Sample size calculation for trials for superiority, non-inferiority, and equivalence. Binomial and . Therefore, it is not necessary to have a large sample size for narrative studies to focus on the in-depth analysis of their stories or narratives (Wells, 2011); instead, it is most important to .
Sample size is one of the important considerations at the planning phase of a research proposal, but researchers are often faced with challenges of estimating valid sample size. Many researchers frequently use inadequate sample size and this invariably introduces errors into the final findings. Many .However, since you can’t know what this percentage is until you actually ask a sample, it is wisest to assume that it will be 50% and use the listed larger sample size. The number of sub-groups (or “comparison” groups) is another consideration in the determination of a sufficient sample size. Statistical power and sample size analysis provides both numeric and graphical results, as shown below. The text output indicates that we need 15 samples per group (total of 30) to have a 90% chance of detecting a difference of 5 units. The dot on the Power Curve corresponds to the information in the text output. However, by studying the entire . In this article, we'll answer these questions about sample size in quantitative research: Why does sample size matter? How do I determine sample size? Which sampling method should I use? What's sampling bias? Why does sample size matter? When sample sizes are too small, you run the risk of not gathering enough data to support your hypotheses or .
Introduction to Sample Size Determination 1 Summary In this chapter, importance of sample size in conducting research has been discussed. Determining sample size in research studies is not only important for the statistical reason but also for the ethical as well as nancial and human resource considerations. (b) For factor analysis appropriate sample sizes depend upon the numbers of items available for factor analysis; for 10 items a sample size of 200 is required; for 25 250; for 90 items 400 and for .
12. Sample size determination in quantitative study Level of precision Range in which the true value of the population is estimated to be This range is often expressed in percentage points (e.g., ±5 percent). Level of confidence or risk based on ideas encompassed under the Central Limit Theorem E.g. a 95% confidence level is selected Degree of variability .

sample sizes for quantitative research
webGive your dog the home it deserves. Shop our selection of dog houses at the Home Depot Canada and get free shipping on select items.
quantitative sample size determination|qualtrics sample size chart